About HeartMate 3 LVAD with Full MagLev Flow Technology
The HeartMate 3™ LVAD, a mechanical circulatory support pump with Full MagLev™ Flow Technology has significantly advanced the field of LVAD therapy, setting the standard with innovation and outstanding clinical outcomes that make a meaningful difference in your patients’ lives.1
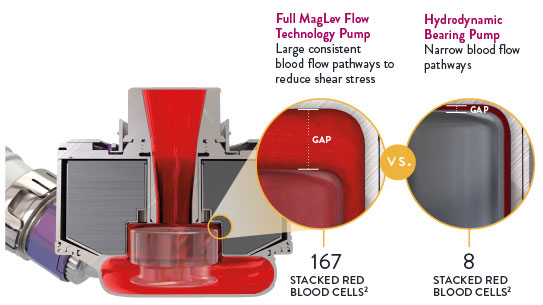
This innovation includes Full MagLev Flow Technology in the pump which maintains gentle blood handling to minimize complications and hemocompatibility-related adverse events.1
The HeartMate 3 LVAD is used for advanced heart failure patients needing short- or long-term mechanical circulatory support.
Sign up to learn about extending meaningful survival with the HeartMate 3 LVAD
- Clinical Data
- Patient Selection
- Case Studies
- Clinician Education

Clinical Outcomes made possible by Full MagLev Flow Technology
Full MagLev Flow Technology maintains gentle blood handling to minimize complications and hemocompatibility-related adverse events.
- Fully levitated, self-centering rotor that does not require hydrodynamic or mechanical bearings
- Large, consistent blood flow pathways to reduce shear stress3
- Intrinsic pulsatility to reduce stasis and minimize thrombus3,4
References
- Mehra M, Uriel N, Naka Y, et al. A Fully Magnetically Levitated Left Ventricular Assist Device-Final Report. N Engl J Med. 2019;380:1618-1627.
- Abbott data on file.
- Bourque K, Cotter C, Dague C, et al. Design rationale and preclinical evaluation of the HeartMate 3 Left Ventricular Assist System for hemocompatibility. Am Soc Artificial Int Organs. 2016;62:375- 383.
- Bourque K, Dague C, Farrar D, et al. In vivo assessment of a rotary left ventricular assist deviceinduced artificial pulse in the proximal and distal aorta. Artificial Organs. 2006;30:638-642.
MAT-2012365 v5.0
