Indications
The device is intended for dilatation of lesions in the renal, iliac, femoral, popliteal, tibial, and peroneal arteries and for the treatment of obstructive lesions of native or synthetic arteriovenous dialysis fistulae.
This device is also indicated for stent post-dilatation in the peripheral vasculature.
Contraindications
- Inability to cross lesion with a guide wire
- Use in the coronary arteries
Warnings / Precautions
- This device should only be used by physicians who are experienced and have a thorough understanding of the clinical and technical aspects of PTA.
- One-time use only – do not resterilize! This single use device cannot be reused on another patient, as it is not designed to perform as intended after the first usage. Changes in mechanical, physical, and/or chemical characteristics introduced under conditions of repeated use, cleaning, and/or resterilization may compromise the integrity of the design and/or materials, leading to contamination due to narrow gaps and/or spaces and diminished safety and/or performance of the device. Absence of original labeling may lead to misuse and eliminate traceability. Absence of original packaging may lead to device damage, loss of sterility, and risk of injury to patient and/or user.
- Do not use if inner package is damaged or opened.
- Employ aseptic techniques during removal from the package and during use.
- Any use for procedures other than those indicated in these instructions is not recommended.
- Use prior to the use by date.
- Carefully inspect the catheter prior to use to verify that it has not been damaged during shipment and that its size, shape and condition are suitable for the procedure for which it is to be used.
- Precautions to prevent or reduce blood clotting should be taken when any catheter is used.
- Flush or rinse all products entering the vascular system with sterile isotonic saline or a similar solution via the guide wire access port prior to use.
- Consider the use of systemic heparinization.
- When the system is introduced into the vascular system, it should be manipulated only under high quality fluoroscopy.
- The Armada™ 35 / Armada™ 35 LL PTA Catheter must always be introduced, moved and or withdrawn over a guide wire (max. 0.035”).
- Never attempt to move the guide wire when the balloon is inflated.
- Never use air or any gaseous medium to inflate the balloon.
- Do not advance the Armada™ 35 / Armada™ 35 LL PTA Catheter against significant resistance. The cause of resistance should be determined via fluoroscopy and remedial action taken.
- The minimal acceptable sheath French size is printed on the package label. Do not attempt to pass the Armada™ 35 / Armada™ 35 LL PTA Catheter through a smaller sized sheath introducer than indicated on the label.
- The size of the inflated balloon should be selected not to exceed the diameter of the artery immediately distal, or proximal, to the stenosis.
- Inflation in excess of the rated burst pressure may cause the balloon to rupture. Use of a pressure monitoring device is recommended.
- When post-dilating stents, use a balloon length that is appropriate for the deployed stent length.
Potential Complications
The following complications may occur as a result of PTA, but may not be limited to:
- Abrupt closure
- Allergic reaction (contrast medium, drug, or device material)
- Aneurysm or pseudoaneurysm in vessel, or at vascular access site
- Angina or coronary ischemia
- Arrhythmias (including premature beats, bradycardia, atrial or ventricular tachycardia, arterial or ventricular fibrillation)
- Arteriovenous fistula
- Bleeding complications requiring transfusion or surgical intervention
- Death
- Detachment of a system component or implantation in an unintended site
- Embolization (air, tissue, plaque, thrombotic material, device)
- Emergent surgery
- Fever
- Hematoma or hemorrhagic event, with or without surgical repair
- Hyperperfusion syndrome
- Hypotension or hypertension
- Infection
- Ischemia or infarction not covered under adverse events
- Myocardial infarction
- Pain (leg, foot, and / or insertion site)
- Peripheral nerve injury
- Pulmonary embolism
- Renal failure or insufficiency
- Restenosis
- Shock
- Stroke
- Target limb loss (amputation of toe, foot, and / or leg)
- Thrombosis or occlusion
- Transient ischemic attack
- Venous thrombosis
- Vessel dissection, perforation, or rupture
- Vessel spasm or recoil
- Worsening claudication or rest pain

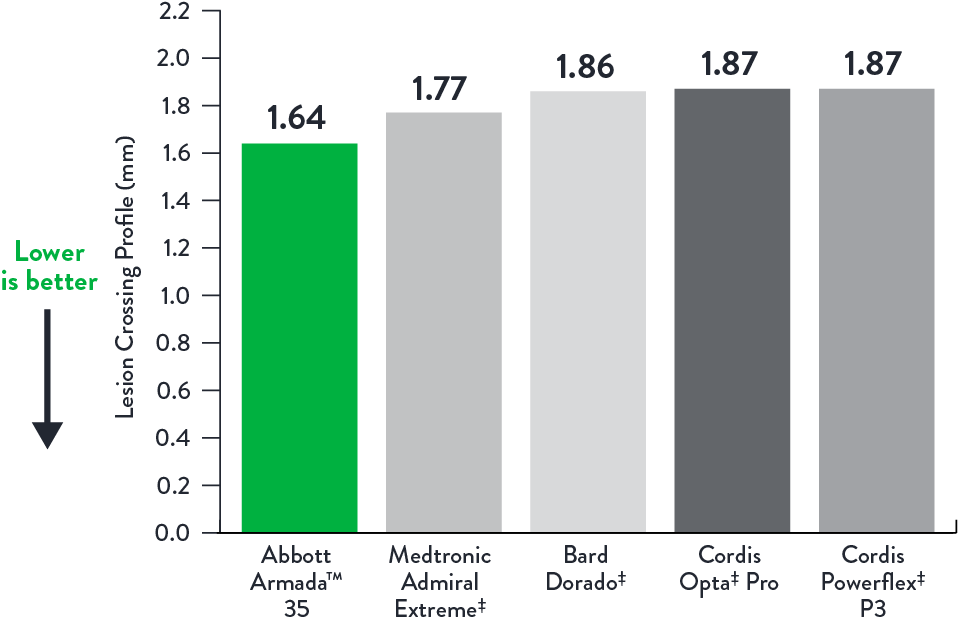
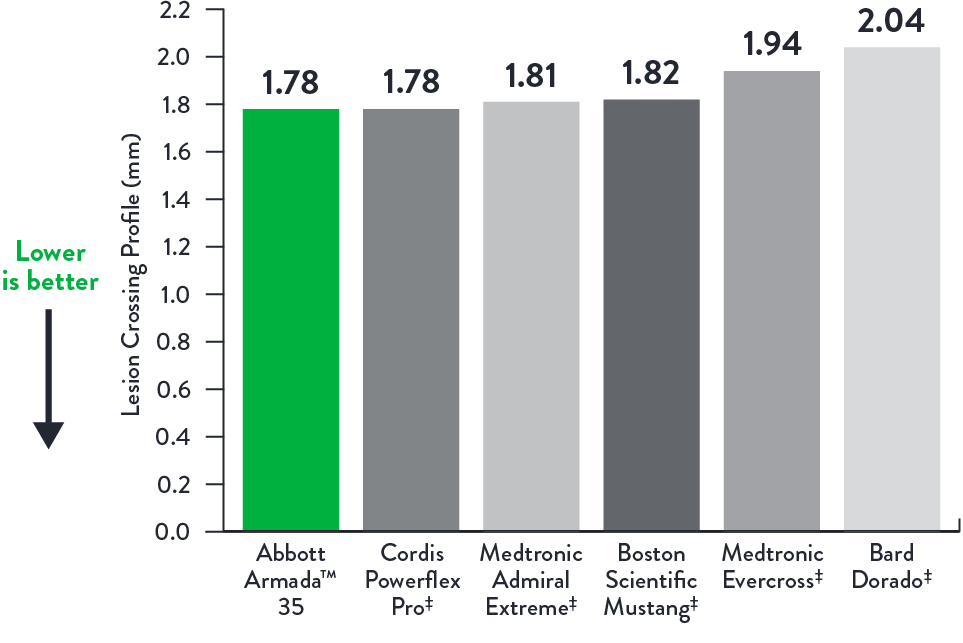
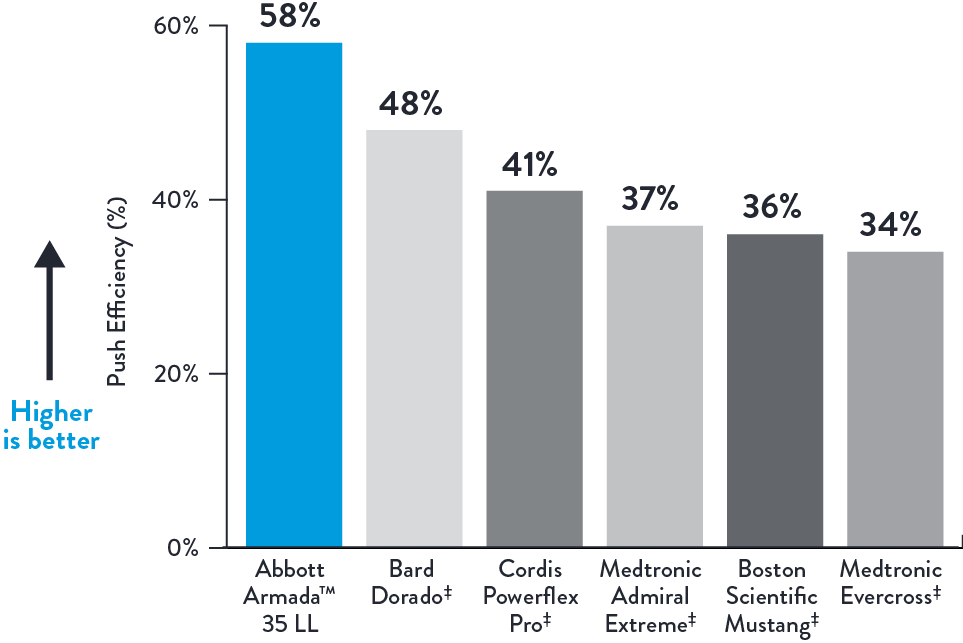

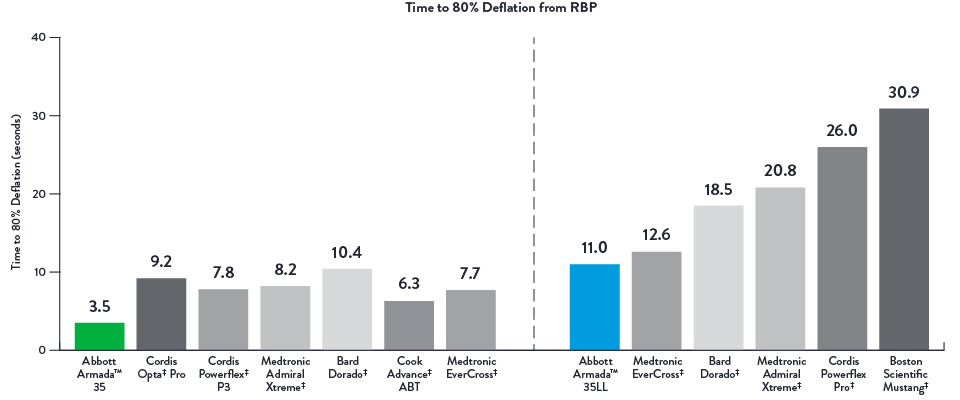




Stay Connected