Coronary artery disease (CAD) develops when plaque—a combination of cholesterol and other substances—builds up in the walls of the arteries that supply blood to the heart and other parts of the body (called atherosclerosis). This buildup of plaque causes the inside of the arteries to narrow over time, which can partially or totally block blood flow to the heart (called myocardial ischemia).1,2
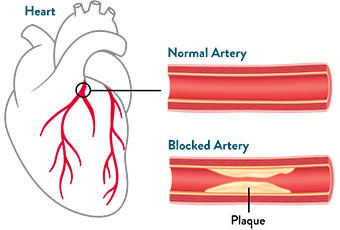
With CAD, the coronary arteries become narrower and harden over many years, reducing oxygen-rich blood flow to the heart.1
Symptoms of coronary artery disease occur when the heart doesn't get enough oxygen-rich blood.1,2
A diagnosis of CAD is based on symptoms, medical and family history, risk factors, and the results from tests and procedures.1
Risk factors for coronary artery disease include:1,2
If you have been diagnosed with coronary artery disease, your treatment will depend on how serious your symptoms are. To help lower your risk for heart attack or worsening heart disease, treatment may include:1,2


MAT-2205023 v1.0
Stay Connected