Understanding Peripheral Artery Disease
Did you know that Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD) is a common condition,1,2 but it's not always diagnosed? And for some patients, this disease can progress to become Chronic Limb Threatening Ischemia which can lead to amputation. The goal for physicians is to try to timely diagnose PAD and treat before it advances to this stage.
If you feel muscle fatigue, cramping and/or pain in your legs during exercise, which stops after resting, you may be experiencing the common symptoms of PAD.4,5 Learn more so that you can have a conversation with your physician.
To learn more about PAD, click on the sections you want to know more about:
What is Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD)?
- PAD is a common condition affecting the legs1,2
- In PAD, a build-up of fatty deposits (plaque) in the leg arteries restricts blood flow from the heart to the legs1,2
- When blood flow is reduced, this can lead to leg pain when walking or climbing stairs because your leg muscles aren't getting enough oxygen2,3
- PAD can also prevent sores on the feet or legs from healing, which can develop into areas of dead tissue (gangrene) that ultimately may lead to amputation of the foot or leg4,5
- PAD may progress to an advanced form known as chronic limb-threatening ischemia (CLTI), incurring significant limb loss, pain, decreased quality of life, and mortality6
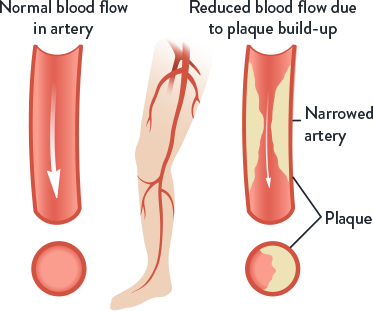
What are the Symptoms of (PAD)?
PAD symptoms don't present the same way in every patient4,5
- In lower leg PAD, symptoms may include muscle fatigue, cramping, and/or pain in the legs during exercises that stop after resting, which is called “intermittent claudication”4,5
- Symptoms of an advanced form of PAD include pain in the toes or feet even while resting, sores on the toes, feet, or legs that don't heal, and leg numbness or weakness4,5
- Symptoms of CLTI include the presence of PAD in combination with pain at rest, gangrene, or ischemic ulcerations persisting for a duration >2 weeks6
Who is at Risk of PAD?
There are certain conditions, known as risk factors, that may contribute to the development of peripheral artery disease (PAD). The risk factors for PAD include:5,8,9
Being Over 65 Years
of Age

Having a Family History
of PAD

Smoking

High Blood Pressure
High Cholesterol

Diabetes

Obesity

How is PAD Diagnosed?
To diagnose PAD, a physical examination is performed. If PAD is suspected, this may be followed by a specific blood pressure measurement.
Physical Examination
- May include an examination of the head, neck, skin, nerves, muscles, heart, lungs, abdomen, lower legs, and feet5
- Measurement of blood pressure, body temperature, breathing, and heart rate5
Ankle Brachial Index (ABI)
When PAD is suspected, an ABI compares the blood pressure in the legs to the arm and is a useful way of confirming PAD diagnosis, especially when symptoms are atypical or absent.1,5,10
How is PAD Treated?
PAD can be managed through a combination of lifestyle changes and various treatments5,11
Lifestyle Changes
including quitting smoking, adapting diet, and practicing regular exercise

Medications
such as medications to treat high cholesterol, high blood pressure, or diabetes

Minimally invasive procedures
such as inserting a small tube (stent) to open blood vessels

Surgery

What should I do Next?
If you have any questions or concerns about PAD or think that you or someone you know may be at risk of PAD, contact your doctor.
Your doctor will ask you to make an appointment with another doctor who specializes in diagnosing and treating PAD, called a vascular specialist.

The information provided is not intended for medical diagnosis or treatment or as a substitute for professional medical advice. Consult with a physician or qualified healthcare provider for appropriate medical advice. This material is intended for use with healthcare professionals only.
References:
- Hirsch AT, et al. JAMA. 2001; 286(11): 1317-24.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD) 27 Sep 2021. Accessed May 2022.
- Cleveland Clinic. Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD). 19 January 2022. Accessed May 2022.
- Shu J, Santulli G. Atherosclerosis. 2018; 275: 379-81.
- Gerhard-Herman MD, et al. Circulation. 2017; 135(12): e686-7256.
- Conte MS, et al. J Vasc Surg. 2019; 70(2): 662.
- Virani SS, et al. Circulation. 2021; 143(8): e254-743.
- Steffen LM, et al. Diabetes Spectr. 2008; 21(3): 171-7.
- Hirsch AT, et al. Circulation. 2006; 113(11): e463-654.
- Criqui MH, et al. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2008; 52(21): 1736-42.
- Wu A, et al. J Am Heart Assoc. 2017; 6(1): e004519.
MAT-2208562 v3.0






