









Every complex case is unique, and no lesion is the same. That’s why we focus on providing the therapies, tools, and specialized knowledge that enable you to tailor your approach and optimize long-term, durable outcomes.

Individualized Solutions for Calcified Lesions
Calcified lesions present unique challenges that can compromise stent delivery and expansion.
Abbott’s specialized solutions for coronary calcium empower you in every step from ACCESS to CLOSE:
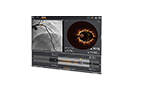
- Assess lesion severity using OCT for clear morphological insights.1
- Prepare and modify tough calcium with dedicated coronary dilatation catheters and atherectomy devices.
- Achieve durable results2 through thorough lesion preparation and evidence-based therapies, even in complex cases as seen in the results of the pivotal ORBIT II trial.

Clear
Evaluate lesion morphology using advanced tools that ensure more accurate and informed decisions.
Calculated
Strategize your treatment and remove obstacles with dedicated solutions to achieve optimal clinical preparation.
Confident
Know your choices are backed by data with strong clinical outcomes and real-world evidence.
References:
- Ultreon™ 2.0 Software Instructions for Use (IFU). Refer to IFU for additional information.
- Lee M, et al. Orbital atherectomy for treating de novo, severely calcified coronary lesions: 3-year results of the pivotal ORBIT II trial. Cardiovasc Revasc Med. 2017;18(4):261-264.
MAT-2501288 v1.0

