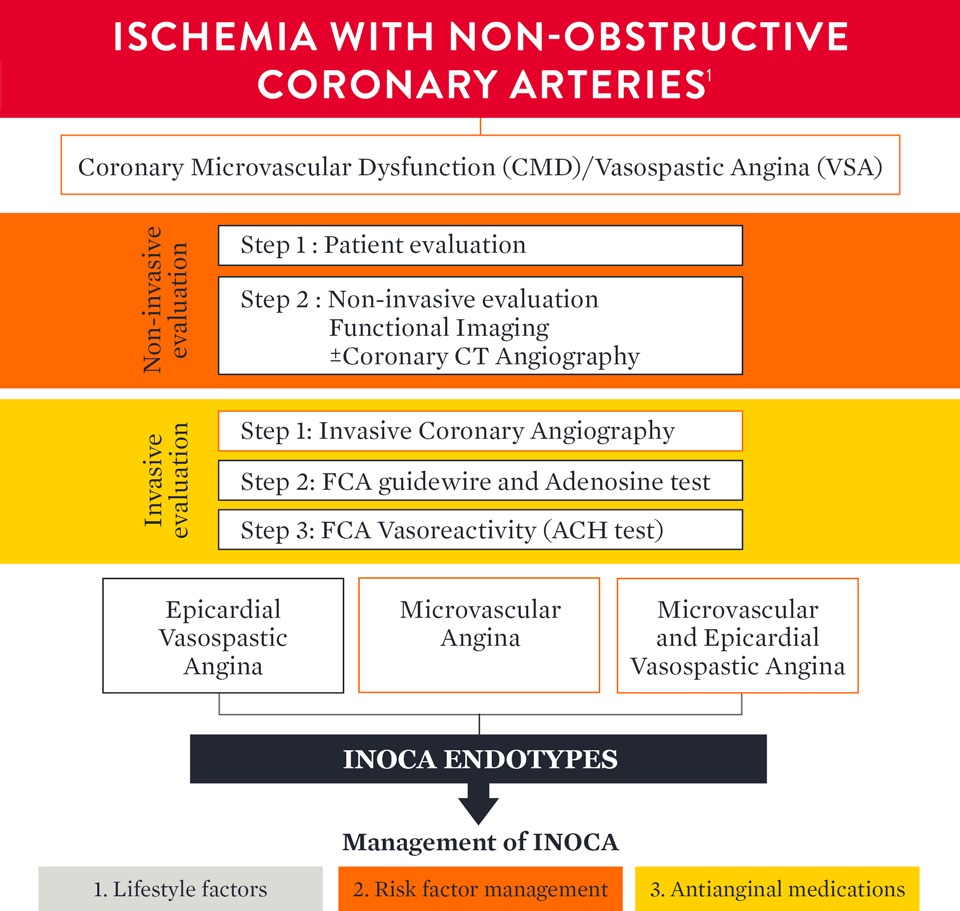
How to Diagnose INOCA
The European Association of Percutaneous Cardiovascular Interventions (EAPCI) Expert Consensus Document defines ischemia and no obstructive coronary artery disease (INOCA) and guidance to its diagnosis and management. The document states that, INOCA patients present with a wide spectrum of symptoms and signs that are often misdiagnosed as non-cardiac, leading to under-diagnosis/investigation and under-treatment.1
Guidelines Recommend Guidewire-Based Measurements
Both European and American guidelines provide a class IIa recommendation for a physiology wire-based assessment for patients with stable chest pain and/or Ischemia and No Obstructive Coronary Artery Disease (INOCA).2,3
The ESC guidelines2 2019 were updated accordingly to include an increased focus on microvascular dysfunction.

The AHA/ACC Clinical Practice Guideline3 on chest pain includes Class IIa recommendation for guidewire-based assessment for ischemia and no obstructed coronary artery disease (INOCA) patients.

CFR = coronary flow reserve; CMR = cardiac magnetic resonance; ECG = electrocardiogram;
FFR = fractional flow reserve; iwFR = instantaneous wave-free ratio; LAD = left anterior descending; PET = position emission tomography.
a Class of recommendation
b Level of evidence
Level-NR: Level (Quality) of Evidence Level B-NR (non-randomized): moderate-quality evidence from 1 or more well-designed, well-executed non-randomized studies, observational studies or registry studies. RCTs. Meta-analyses of such studies.
INOCA is Not Benign: Coronary Microvascular Dysfunction — Why Diagnosis In the Cath Lab Does Matter
EAPCI CONSENSUS DOCUMENT ON INOCA
Aladie Chieffo MD, Milan, Italy
An updated standardization of Coronary Microvascular Dysfunction (CMD) criteria is provided by the COVADIS group including the cut-off values of CFR < 2.0 and IMR ≥ 25 that characterize CMD.1
| Criteria | Evidence | Diagnostic Parameters |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Symptoms of myocardial ischaemiaa |
|
| 2 | Absence of obstructive CAD (<50% diameter reduction or FFR >0.80) |
|
| 3 | Objective evidence of myocardial ischaemiab |
|
| 4 | Evidence of impaired coronary microvascular function |
|
Kunadian et al. European Heart Journal. 2020; 0:1-21.
Definitive microvascular angina is only diagnosed if criterias 1, 2, 3 and 4 are present.
CAD = coronary artery disease; CCTA = coronary computed tomographic angiography; CFR = coronary flow reserve; ECG = electrocardiogram; FFR = fractional flow reserve; IMR = index of microcirculatory resistance.
a Many patients with heart failure with preserved ejection fraction would fulfil these criteria: dyspnoea, no obstructive CAD and impaired CFR. For this reason, consider measuring LV end-diastolic pressure (normal ≤10 mmHg) and NT-proBNP normal <125 pg/mL.
b Signs of ischaemia may be present but are not necessary. However, evidence of impaired coronary microvascular function should be present.
How to Diagnose CMD with a Comprehensive Physiology Assessment
The PressureWire™ X Guidewire and CoroFlow‡ Cardiovascular System is a comprehensive solution for assessing both epicardial arteries and the microvasculature.4
How to Measure IMR
Allen Jeremias, MD, New York, USA
Diagnosis With Comprehensive Physiology Indices
Colin Berry MD, PhD, Glasgow, UK
The PressureWire™ X Guidewire has pressure and temperature sensors that communicate with the CoroFlow‡ Cardiovascular System to provide a comprehensive physiology assessment4

How to Treat Patients with CMD: Results of the CorMicA Trial
Microvascular angina and vasospastic angina are the two most common causes of INOCA, and both types of angina can be identified with diagnostic testing. The randomized CorMicA trial provides a diagnostic and treatment approach.5
The trial protocol assessed patients to determine:
- Microvascular angina or CMD—using the PressureWire™ X Guidewire
- Vasospastic angina—with acetylcholine testing
CorMicA Findings
Colin Berry MD, PhD, Glasgow, UK
The CorMicA results indicate a role for a more thorough investigation of coronary microvascular dysfunction among patients with INOCA, as well as an opportunity to better tailor patient treatment.5
CorMicA Trial 1-year RCT Outcomes5

INOCA PATIENT MANAGEMENT
The EAPCI Expert Consensus Document1 defines INOCA and provides guidance to the clinical community on the diagnostic approach and management of INOCA based on existing evidence and best current practices.

Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor = ACEI
Angiotensin receptor blocker = ARB
References
- Kunadian, V., et al. EAPCI Expert Consensus. Eur Heart J 2020;0:1-21.
- Knuuti, J., et al. 2019 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of chronic coronary syndromes. European Heart Journal 2020:41,407-477.
- Gulati, M., et al. 2021 AHA/ACC Guideline for the Evaluation and Diagnosis of Chest Pain. Circulation 2021;144e368-e454.
- PressureWire X Guidewire Instructions for Use (IFU). Refer to IFUs for additional information. CoroFlow Cardiovascular System IFU.
- Ford, TJ., et al. 1-year outcomes of angina management guided by invasive coronary function testing (CorMicA). J Am Coll Cardiol Intv. 2020;13:33-45.
MAT-2112674 v2.0




