The Supera™ Stent has been studied in over 2,000 patients worldwide in the SUPERB trial and 16 retrospective studies. Notably, in all of the 17 studies, the Supera™ Peripheral Stent showed durable results with zero fractures at 1 year.1,4-19
At 1 year the Supera™ Stent demonstrated primary patency of 91% when nominally* deployed. At 3 years, freedom from targeted lesion revascularization (TLR) was 94% when nominally* deployed.1
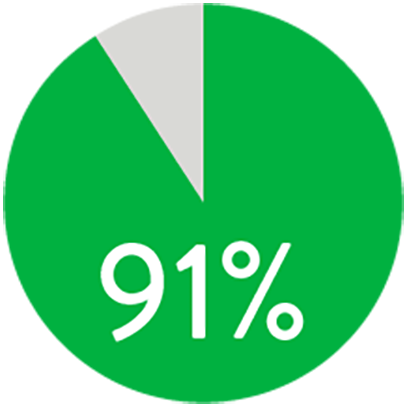
PATENCY (K-M) AT 1 YEAR
When nominally deployed*
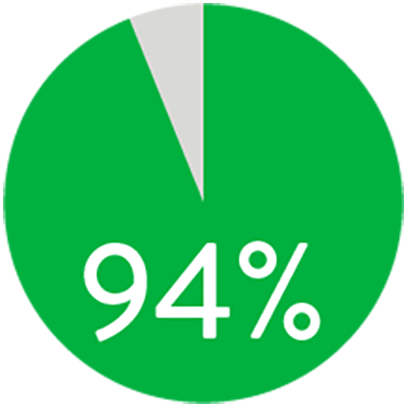
FREEDOM FROM TLR AT 3 YEARS
When nominally deployed*
*Nominal deployment is defined as the stent length upon deployment being within +/- 10% of the labeled stent length. This data is from a non-powered post-hoc analysis. K-M=Kaplan Meier.
With some peripheral stents, increasing lesion lengths can lead to decreasing patency rates.20 The Supera™ Stent stands apart for its consistently high patency rates in lesions spanning lengths from 5.3 cm up to 28.0 cm.†
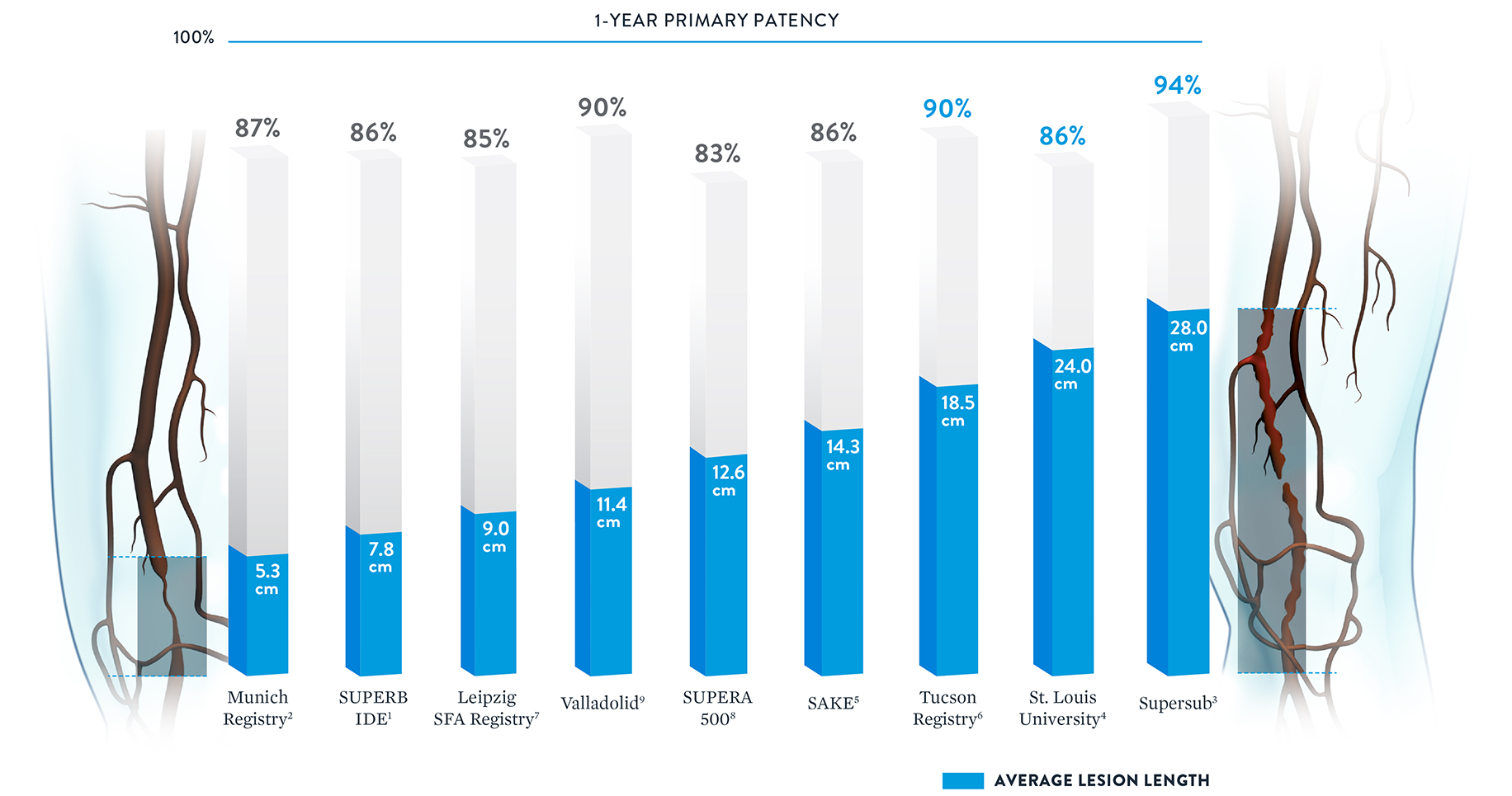
† Published data was included if lesion length and patency were both available.
Note: Results from different clinical trials are not directly comparable. Information provided for educational purposes only.
Whether treating simple (TASC A&B) or complex (TASC C&D) lesions, the Supera™ Stent is associated with impressive, consistent patency performance data at 1 year.1-4
| Simple | |||
|---|---|---|---|
 | Trial/Study | MUNICH REGISTRY2 | SUPERB1 |
| Lesion Length | 5.3cm | 7.8cm | |
| TASC A&B Lesions | 100% | 94% | |
| 1-Yr Patency | 86.7% | 90.5% | |
| Sites | Single Center | Multicenter (46 sites) | |
| # Patients | 70 | 264 | |
| Complex | |||
|---|---|---|---|
 | Trial/Study | ST. LOUIS4 | SUPERSUB3 |
| Lesion Length | 24cm | 28cm | |
| TASC C&D Lesions | 78% | 100% | |
| CTOs | Unknown | 100% | |
| 1-Yr Patency | 85.6% | 94.1% | |
| Sites | Single Center | Single Center | |
| # Patients | 48 | 34 | |
TASC: Trans-Atlantic Inter-Society Consensus
MAT-2106532 v2.0
You are about to enter an Abbott country- or region-specific website.
Please be aware that the website you have requested is intended for the residents of a particular country or countries, as noted on that site. As a result, the site may contain information on pharmaceuticals, medical devices and other products or uses of those products that are not approved in other countries or regions
Do you wish to continue and enter this website?
MAT-2305078 v1.0