The market-leading Agilis NxT Steerable Introducer is now compatible with larger catheters to support all therapy deliveries from PFA to RF to CRYO - for an optimal workflow with our One System Solution. Introducing the Agilis NxT Steerable Introducer, Dual‑Reach™ (13 Fr).
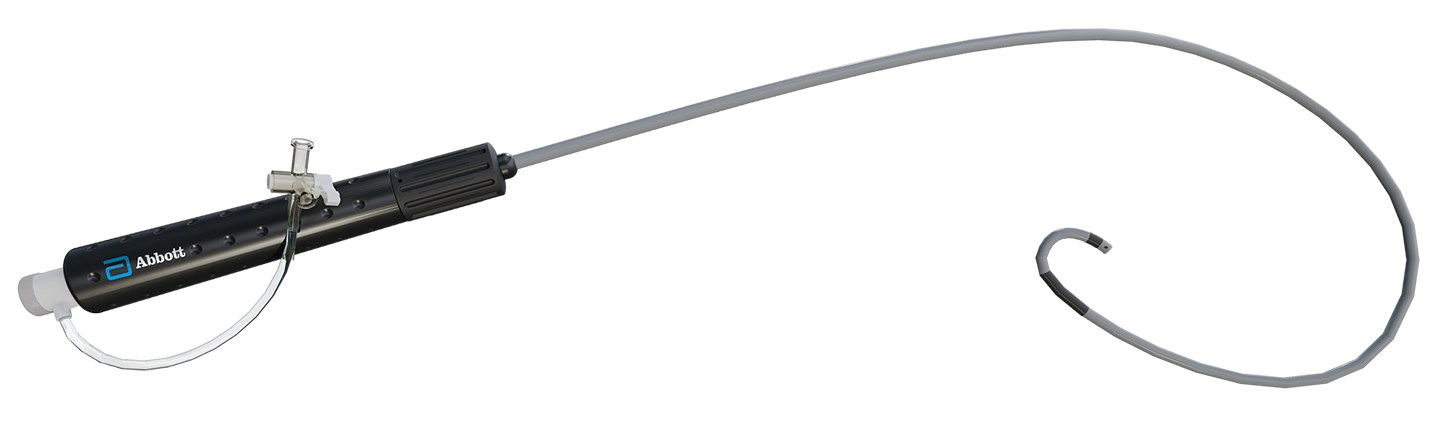

ATRAUMATIC TIP
New low-profile design and atraumatic tip
SIX OFF SET VENTING HOLES
Smaller diameter (.030”) and 90º set reduces the likelihood of guidewire exiting through side holes
RADIO-OPAQUE TIP MARKER
Ring of platinum iridium enables visualization under fluoro; 4 mm from tip
SHEATH TO DILATOR FIT
Low-profile design with lower transeptal crossing force
BRAIDED SHAFT
Provides exceptional torquability, pushability and kink resistance with Dual-Reach™ bidirectional 180˚/90˚ deflection to allow asymmetric deflection for more mobility
BI-DIRECTIONAL; ROTATING COLLAR
To deflect the tip clockwise ≥180° and counterclockwise ≥90° auto locking
HEMOSTASIS VALVE
3-way stopcock for air or blood aspiration, fluid infusion, blood sampling
As evidenced in more than one million procedures*, for a growing number of physicians, Agilis NxT Steerable Introducer (8.5 Fr) is the introducer of choice when guiding ablation catheters to treat arrhythmias. Tailor to your patient’s anatomy with a large variety of sizes and curves that maintain their shape
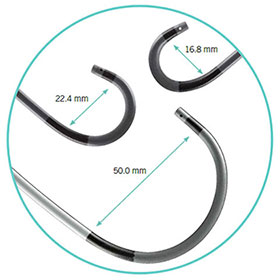
Curves shown is for 8.5 Fr Agilis NxT Steerable Introducer
Enhanced catheter stability enables control of tip movements within millimeters along the intended ablation line1
Access hard-to-reach areas with precise maneuverability and auto-lock steering, such as the right inferior and left anterior pulmonary veins1

Greater catheter-tissue contact force, which may support more durable lesion formation2
Greater freedom from arrhythmia at 6 months (76.0% vs 53.0%)3 and 18% greater at 12 months (74.0% vs 62.7%)4
Complete PVI isolation (left- and right-sided veins) (43 pts vs 8 pts)1
Fewer re-do ablations (6 pts vs 23 pts)1 and 17% fewer acute PV reconnections (50% vs 60%)5

*Based on sales through Dec 31, 2020
MAT-2413464 v1.0
Stay Connected