Talk to a Patient Ambassador
Get a firsthand account of what life is like after LVAD by connecting with our HeartMate patient ambassadors.
Welcome to the Abbott cardiomyopathy FAQ section, we know cardiomyopathy often plays a significant role in heart failure and we are here to help you find answers to your common questions about this heart condition, including its symptoms, types, treatments, and more.
Cardiomyopathy in general refers to diseases of the heart muscle. These diseases change your heart muscle in ways that make it not pump well. This can include enlarging your heart muscle or making it thicker and more rigid than normal. These changes affect how well the heart can pump blood throughout your body, which often can advance to heart failure as it progresses.
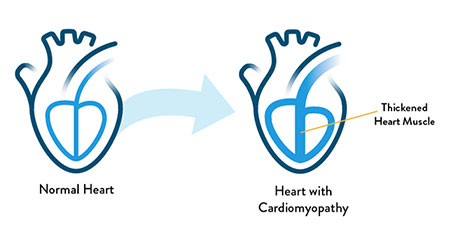
Causes of cardiomyopathy vary but can include factors such as genetics, long-term high blood pressure, heart tissue damage from a previous heart attack, chronic rapid heart rate, lifestyle choices, and even certain infections. Sometimes, the cause is unknown. During your heart screening, your doctor will discuss these factors with you.
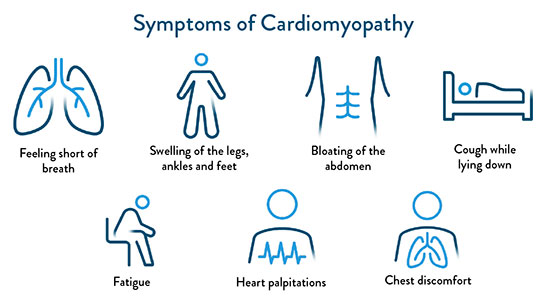
It’s important to note that the symptoms of cardiomyopathy might not be noticeable in the early stages. As the condition gets worse, symptoms typically include feeling short of breath, swelling of the legs, ankles and feet, bloating of the abdomen, cough while lying down, fatigue, heart palpitations, and chest discomfort. If you are experiencing these symptoms, it is important for you to reach out to your physician’s office as soon as possible.
Diagnosis involves a physical exam, family medical history, and tests such as echocardiogram, MRI, ECG, blood tests, and sometimes a biopsy of the heart muscle.
There are several types of cardiomyopathy, including:

Treatment for cardiomyopathy typically aims to manage symptoms and slow the disease's progression. Options may include medications, lfestyle changes, medical devices like pacemakers or LVADs and heart transplant. If you are diagnosed with cardiomyopathy your physician will speak with your about the treatment options that are available to you. If you are in need of a heart failure specialist, you can enter your location and find one near you.
While lifestyle changes can slow the progression of the condition, it will assist in managing symptoms and improving quality of life. Some lifestyle changes that may impact your cardiomyopathy journey include: a low sodium diet, alcohol moderation, avoiding smoking, regular exercise, and managing stress.

In many cases, cardiomyopathy has a genetic component that makes certain individuals more likely to have it. If you have a family history of cardiomyopathy or heart failure, genetic testing and regular screenings may be recommended by your healthcare team.
These materials are not intended to replace your doctor’s advice or information. For any questions or concerns you may have regarding the medical procedures, devices and/or your personal health, please discuss these with your physician.


MAT-2413785 v1.0
Stay Connected